Anyone who sets a goal to lose weight begins to look for a magical set of exercises for weight loss: how to burn more, exercise less and not give up the usual sweets and fast food.
It is important to understand that playing sports for weight loss is a competent combination of physical activity and proper nutrition. As some trainers say, all training begins in the kitchen.
Today we will understand the subtleties of competent training, exercises and performance techniques, building a typical training week and adjusting the diet.

How to exercise to lose weight
There is no universal set of exercises that are suitable for everyone and guarantee weight loss in the shortest possible time. However, you can create your own planning structure based on several key principles and already in it choose those exercises that are more suitable based on technical, physical and time capabilities.
What is recommended to pay attention to if the goal of training is to lose weight:
- Combine strength and cardio training. You are not on a mission to become a bodybuilder or a marathon runner, so you should not go to extremes. Find a happy medium by spreading the workload evenly throughout the week.
- Alternative training in different directions. This way you will have enough time to recover the muscles involved - you can train more often and more. For example, if your plan is to run on Monday, do arm strength on Tuesday and bike on Wednesday.
- Don't exercise when you're tired. If you had a hard day at work, didn't get enough sleep, or had a long flight on a business trip, you don't have to go to an evening workout at all costs. Despite the supercompensation effect promoted by motivational videos (increasing the initial level of physical capabilities after intensive training), it will only work against the background of normal recovery, including nutrition and sleep.
- Adjust your diet for your workouts. You should not train on an empty stomach, especially if you do not have the relevant experience, but you should not go to training immediately after breakfast. The optimal time for classes is two to three hours after a meal.
- The most effective for burning fat are considered interval training, in which periods of intense load alternate with short periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. One option for interval training could be circuit training at the gym, where intense strength exercises are alternated with short bursts of cardio, such as jogging or brisk walking.
- Don't expect instant results. There is no need to weigh yourself every day and watch the deviations in grams, evaluating the progress. Untrained people usually need six to eight weeks to adapt to exercise, after which their fitness level allows for the addition of high-intensity exercise and longer workouts that burn more calories and fat.
- For a beginner, 300 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week will be sufficient. These include: brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, strength and circuit training in the gym, jumping rope, outdoor exercise equipment, walking on hills and trails. Spread the load evenly over the days. It could be five one-hour workouts a week, or three one-hour sessions on weekdays and a long two-hour bike ride on the weekend.

Complex of exercises for weight loss
Let's take the average person who works a standard 5/2 schedule and only has the opportunity to work out after work on weekdays as well as weekends.
Since sports performance plays a secondary role in losing weight, you should not train on both weekends. Allow yourself a day for complete rest. Firstly, it is necessary to recover physically after a working week, and secondly, this will allow you to take a mental break from the training process, which will now permeate the weekly schedule in pursuit of weight loss.
Examples of a training week:
| Day of the week | Option 1 | Option 2 | Option 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Strength training in the gym | Strength training in the gym | Light cardio workout |
| Tuesday | Light cardio workout | Outdoor training | Strength training in the gym |
| Wednesday | Relaxation | Relaxation | Circuit training |
| Thursday | Strength training in the gym | Light cardio workout | Relaxation |
| Friday | Circuit training | Strength training in the gym | Strength training in the gym |
| Saturday | Continuous cardio | Relaxation | Continuous cardio |
| Sunday | Relaxation | Continuous cardio | Relaxation |
Strength training in the gym
Strength training, including resistance training, helps increase muscle tone, increase strength, and build muscle mass over time. Weights include dumbbells, barbells, weights, expanders and various simulators.
Strength training is important because it allows you to maintain muscle mass and strength while shedding excess fat. They have also been shown to increase bone density, which in turn reduces the likelihood of developing osteoporosis with age.
Examples of effective fat burning exercises in the gym:
Lift dumbbells
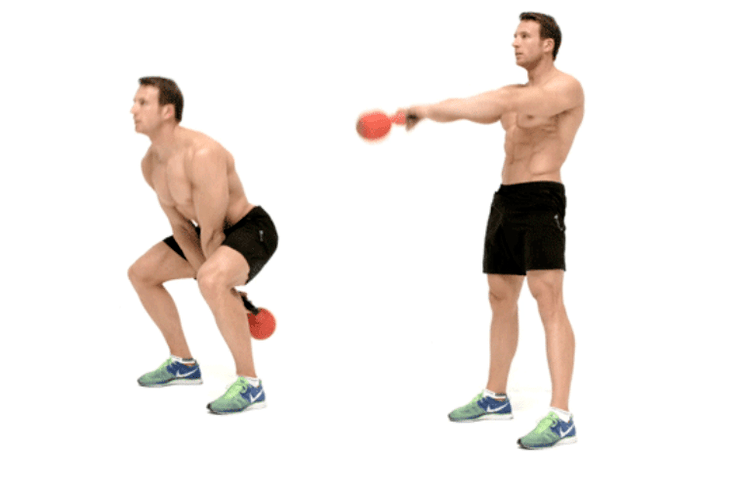
Dumbbell deadlifts are relatively easy to learn and one of the most effective fat-burning exercises because they engage the glutes, thighs, abs, back, arms and shoulders at the same time.
Technique:
Stand straight with feet slightly wider than shoulders and knees slightly bent. Hold the weight with both hands between your legs. Lean back a little, straighten your legs at the same time and take the dumbbell forward with straight arms. The weight itself will do the opposite movement. Your task is to slightly bend your knees and drop it like a pendulum back. Each swinging movement is made from the legs to the arms.
Typical errors:
- Do not round your back, it should be straight.
- Do not try to pull the dumbbell up. All swings are done by momentum due to movements given by the legs.
- Do not carry the dumbbell too far forward. This will put more stress on the shoulder joints and can lead to injury.
- Don't take too much weight. The point of the exercise is to involve a large number of muscles and technically correct execution, not to lift a significant weight.
Squats with dumbbells
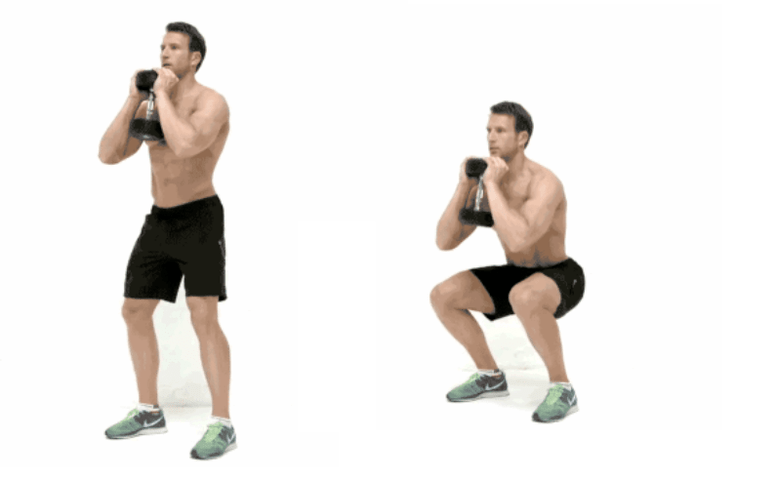

Squats are a basic exercise for leg development. If squatting with your own weight is easy for you, but you are afraid to switch to barbell training, start with an easy option - dumbbell squats. This exercise, in addition to the legs, includes the back, abdomen and arms.
Technique:
Stand up straight. The feet are slightly wider than the shoulders. Grasp a dumbbell with both hands at one end and raise it to chest level. Begin squatting until your thighs are parallel to the floor. Slowly stand up to starting position. The legs must be still.
Typical errors:
- Heels off the floor. If you start jumping up and down to get to the starting position, you've picked up a dumbbell that's too heavy.
- Don't round your back. Stand straight both above and below.
Dumbbell or dumbbell overhead press
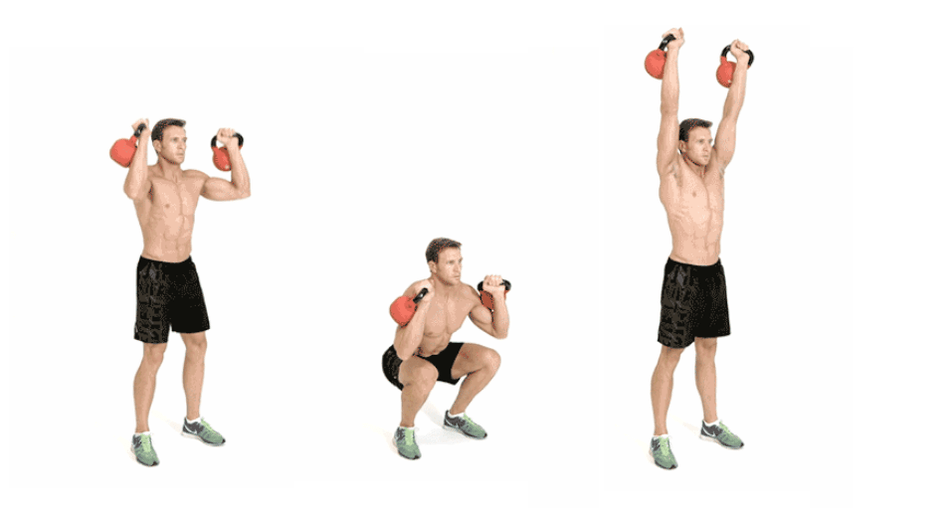

This exercise can be performed both statically and dynamically, combining bench presses with squats, which will allow you to burn even more calories and fat. In the dynamic version, almost all the main muscle groups are included - buttocks, thighs, back, abdomen, arms, shoulders.
Technique:
Stand straight, feet slightly wider than shoulders. Hold a dumbbell or dumbbell in each hand. Bend your elbows, the shells should be above your shoulders. Squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor. As you stand up in the starting position at the top, squeeze the dumbbells / kettlebells above your head. Return your hands to their original position.
Typical errors:
- Do not take too heavy shells. It is easy to injure yourself in dynamics, therefore, at the stage of getting used to and mastering the technique, it is better to work with the lightest dumbbells / kettlebells.
- Do not lift your heels off the floor as this will compromise stability - you may lose balance due to the extra weight in your arms.
- Do not grip dumbbells/weights after standing up. Use the momentum you set with your feet from the bottom point. All movements are performed in dynamics, as in a kettlebell swing exercise.
farm walk
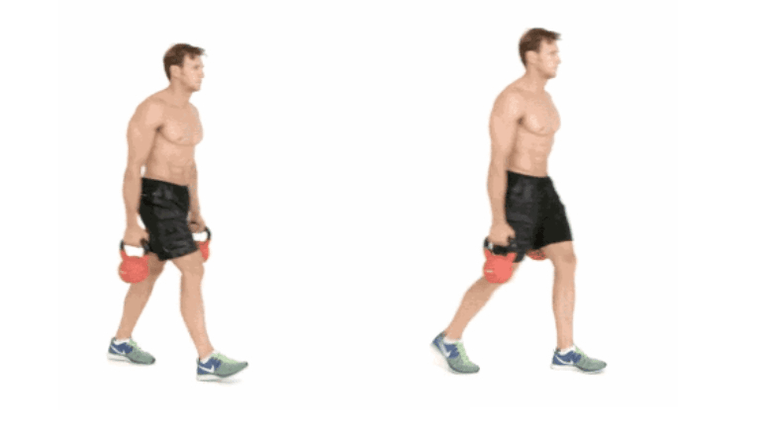
The farmer's walk is a weighted walk. This exercise, due to the additional weight, increases the load on the legs and also involves the shoulders, arms, back and abdomen.
First, take a pair of dumbbells or dumbbells with a total weight of 25-30% of your body weight and take 20-40 steps. If it's easy, you can add weights or make the exercise more difficult and do a jump.
Dumbbell bench
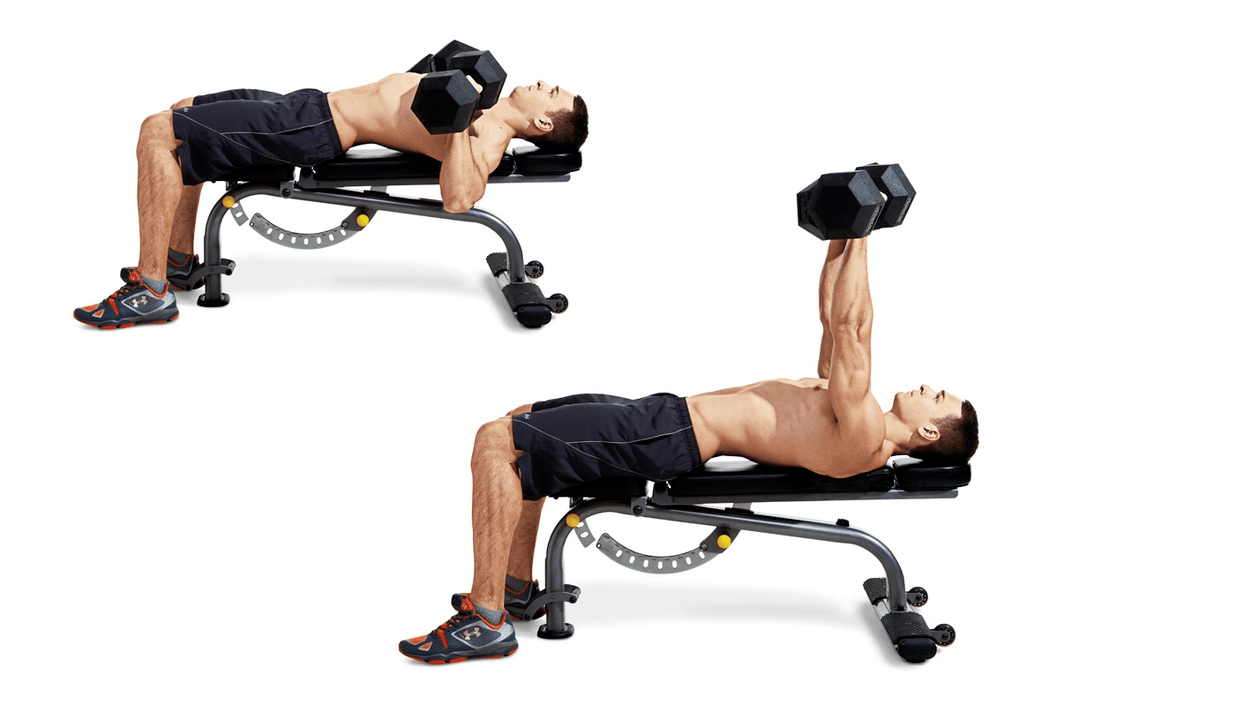

The bench actively involves the upper body - pectoral muscles, shoulders, arms.
Technique:
Take a dumbbell in each hand and lie on a bench. Spread your feet slightly wider than your shoulders and press your heels firmly into the floor. Tighten your abdominal and back muscles. Push the dumbbells up from your chest until your arms are straight. Slowly return them to their original position.
Typical errors:
- Don't let go of your hands when moving down. This can lead to shoulder injury.
- Do not take dumbbells that are too heavy, as this also increases the rate of injury. You should be comfortable doing 8-12 reps per set.
Circuit training
The good thing about circuit training is that you can incorporate almost any exercise that you can do at a moderate or fast pace.
The main points to keep in mind when planning a circuit workout:
- Alternate exercises for different muscle groups to take turns resting your arms, legs, back, and abs.
- The duration of the intense interval should not exceed one minute, otherwise the exercise will turn into endurance work. It is important to perform this interval at a fast or moderate (in the case of weight training) pace.
- The duration of the low-intensity interval (walking, jogging) or rest should not exceed 30 seconds.
- The total duration of the workout should be 15-20 minutes.
Examples of exercises:
- pushups;
- raising bent legs hanging on the horizontal bar;
- squats;
- dynamic core exercises - rock climbing, bicycle;
- stretching - jumping lunges with a change of legs;
- incline dumbbell row;
- swinging weights;
- overhead dumbbell press;
- burpees;
- push-ups on uneven bars;
- jumping on the box;
- jumping rope;
- alternating plank leg raises.
Assemble a block of four to eight exercises in one round. Each exercise is performed for 30-60 seconds with 30 seconds of rest. Rest between rounds - one to two minutes or light jogging if you train outside or the gym allows. Complete three to five circuits until the total workout time is closer to 15-20 minutes.
Light cardio workout
Light cardio is low to moderate intensity exercise that lasts no more than an hour. For beginners, it is best not to do more than 30 minutes until you feel that your cardiovascular system has adapted enough to be able to exercise without holding your breath.
One of the markers of cardiovascular fitness is the speaking test. If you can hold a conversation while doing cardio, then the intensity of the load will allow you to train long enough.
Light cardio includes:
- jogging;
- pedals on an exercise bike or bicycle;
- stepper classes;
- jumping rope;
- swimming;
- skiing.
Continuous cardio
Long workouts differ from easy ones only in the time spent. Aim to maintain the same intensity that allows you to complete the speaking test.
To combine business with pleasure, join a running club for weekend runs, cycle with friends in the countryside or go for long hikes over hills and rough terrain.
Typical errors:
- Don't start too fast. You don't have to go out right away. Instead, start your run with a brisk walk and slowly transition to running. When you ride a bike, don't climb the mountain right away, but ride for 10-20 minutes on a smooth road at a leisurely pace.
- Don't train strictly on time. Focus on your own feelings. No need to strain if you are tired.
- Do not forget to drink water or isotonic drinks, especially in summer. During prolonged exercise, the body loses fluid through sweat, so these losses must be replaced.
Exercise tips
- Every workout starts with a warm-up and ends with a cool-down. Warming up is necessary to warm up the muscles and reduce trauma, hanging - for smooth cooling and reducing blood circulation in the body.
- Don't train the same way two days in a row. Let your muscles rest.
- If you can't do a certain exercise, replace it with a similar one. Instead of running, you can walk on a stepper, instead of a press with dumbbells, do push-ups from the floor, instead of pull-ups, do pull-ups in a block simulator. The same muscle group can be loaded with a bunch of different exercises.
- Start with light weights and gradually increase the load. Linear progress is only at the beginning, after that it will be more difficult for you to add weights as it will take longer for the ligaments, tendons and muscles to adapt. Excessive zeal and desire to shake the bar more can lead to serious injuries and forced interruption of training.
- If you feel that you are very tired, take a break for two to three days to allow the body to recover. Periodically organize an unloading week, for example, once a month, when the load is 50-75% of the usual. In the unloading week, you can eliminate one or two workouts or simply reduce the time of each session by 15-30 minutes.

Diet tips for weight loss
- Breakfast should be healthy and rich in slow carbohydrates: cereals, whole grains, bananas. Carbohydrates are not only fuel for working muscles (carbohydrates from food are stored in the muscles and liver in the form of glycogen), but also a source of glucose for normal brain function.
- Don't look for a quick fix in the trendy low-carb and keto (high-fat) diets. Stick to your doctor's recommended balance of protein (10-30%), fat (25-35%) and carbohydrates (45-65%) and adjust your diet according to how you feel.
- To lose weight, you need to be in a calorie deficit. This means that you should spend a little more than you consume. Consumption includes the body's average needs for normal functioning, as well as calories burned during exercise. Consumption should be reduced evenly in all components (proteins, fats and carbohydrates), and not at the expense of one, as is usual, for example, in a low-carbohydrate diet.
- If you want to calculate everything exactly, install an application on your phone in which you will enter all the food eaten during the day. Special applications have their own database, where certain calories and BJU balance are registered for each product. Over time, you will understand where you can cut excess calories without harming the body.
- Pre-workout nutrition should be sporty – focus on foods that provide enough energy for exercise. Avoid "empty" calories from fast food and sugary drinks.
- Post-workout meals should include foods rich in protein and slow carbohydrates to ensure muscle recovery and energy reserves. For these purposes are suitable: cottage cheese and fruit, salad with chicken or cheese, sandwich with turkey and fresh vegetables, chicken breast with rice.
- Drink enough water. Losing weight through dehydration is not the best idea, especially when you sweat profusely during exercise. At the same time, forcibly pouring two or three liters of water into yourself is also not worth it. The body will only tell you when you need to replace the lost fluid.















